Michelle Sun

Daniel Blazquez
Securing secrets is a difficult task. Developers frequently hardcode credentials for quick testing or use AI-generated code snippets that include live API keys or tokens. This means that enterprise secrets can inadvertently make their way into repositories and pipelines, exposing organizations to security and compliance risks without anyone noticing. When a secret is committed to a repository, it spreads quickly across branches, becomes difficult to track, and leads to leaks that are hard to clean up. These exposures give attackers potential entry points into critical production environments.
Datadog Secret Scanning, now generally available, helps you detect, validate, and block exposed credentials before they compromise your environments. As part of Datadog Code Security, Secret Scanning continuously monitors your source code, repositories, and CI/CD pipelines for credential leaks and integrates directly into developer workflows for shift-left security and fast remediation.
In this post, we’ll show how Secret Scanning helps you:
- Prioritize exposed credentials with live third-party validation
- Block secrets from being committed or merged
Prioritize exposed credentials with live third-party validation
Not all detected secrets pose the same level of risk. Traditional scanners treat every potential credential as a high-priority leak, overwhelming security teams with false positives.
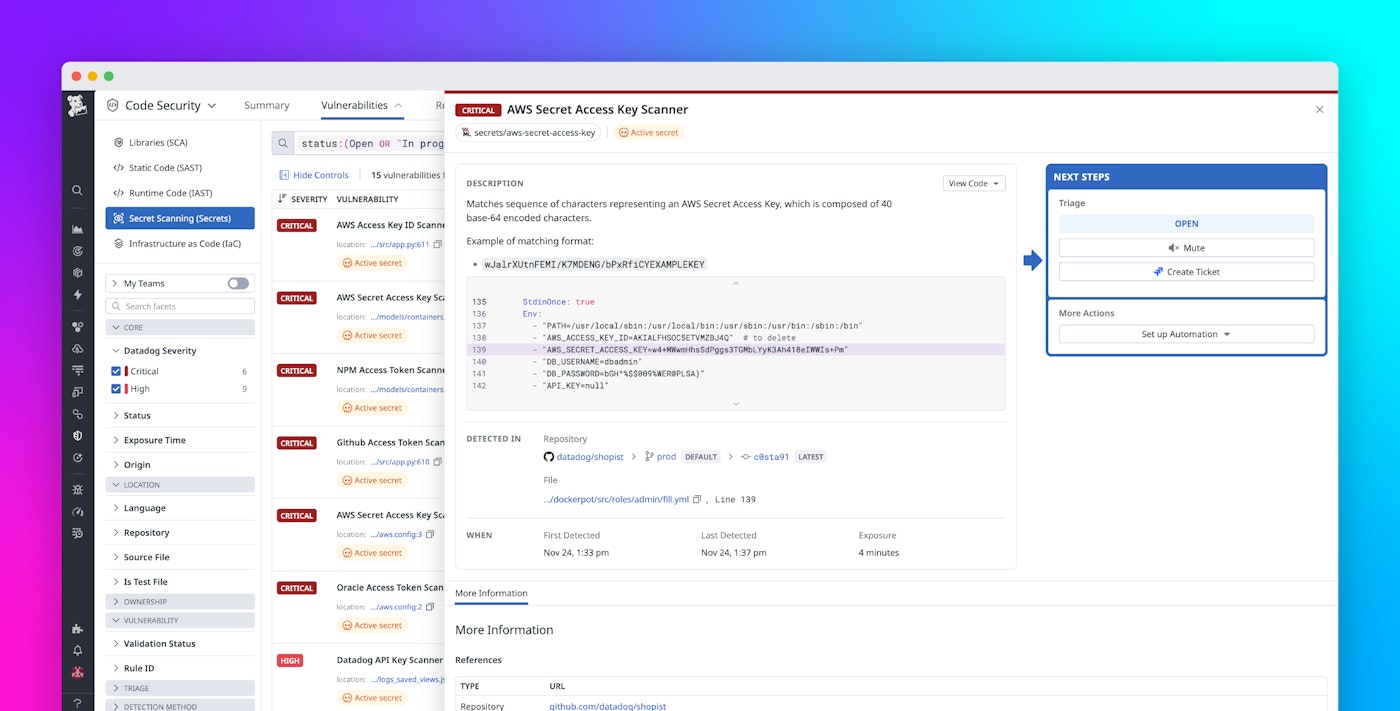
When Secret Scanning finds a potential secret, Datadog automatically verifies the secret with the corresponding third-party provider (such as AWS, GitHub, or OpenAI) to determine if the credential is actually active. Live validation lets you focus remediation efforts on real, active credentials that attackers could exploit.
For example, a GitHub API token that is found in a commit might appear valid syntactically but already be deactivated. Datadog’s live validation can programmatically tell the difference between active and inactive credentials, reducing alert fatigue and helping security teams zero in on what matters. These verified findings are surfaced directly in Code Security, where developers can see the validation status, severity, and code context of the detection.
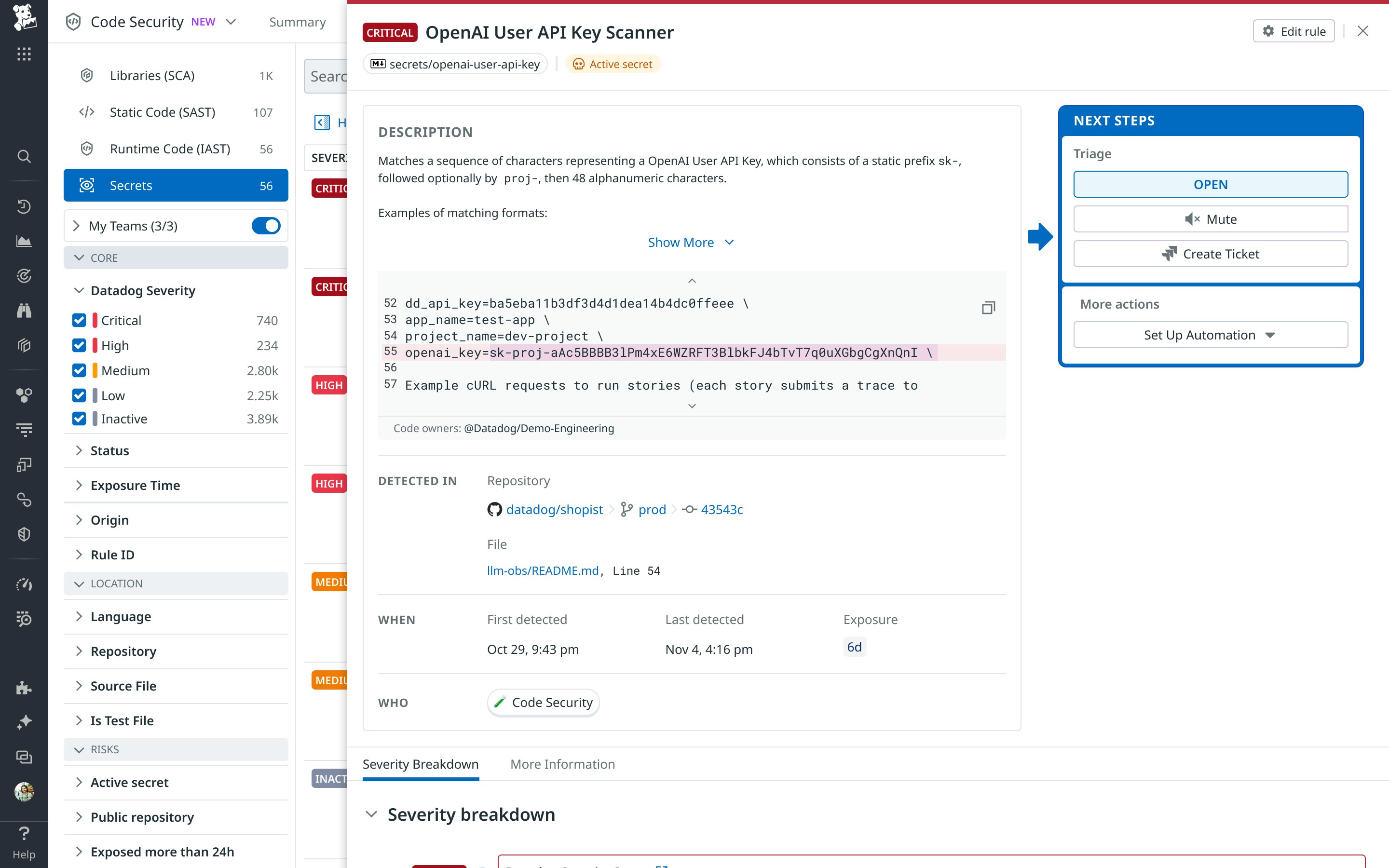
This approach cuts down time wasted on false alarms and enables you to make confident, data-driven decisions about what to fix first.
Block secrets from being committed or merged
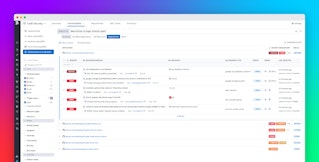
Beyond detecting leaked credentials, Secret Scanning proactively prevents secrets from being introduced into your codebase. By integrating directly with your CI/CD workflows, Secret Scanning enforces pre-commit and pre-merge checks that stop keys from ever entering your repositories.
When a developer attempts to commit or merge a change that introduces an exposed credential, Secret Scanning automatically blocks it and alerts the user. This shift-left, real-time protection prevents live secrets from propagating and helps you maintain a clean, compliant codebase without slowing down development.

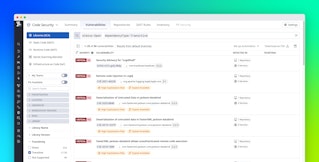
And because Secret Scanning is integrated with the Datadog platform, you can correlate secret exposure data with runtime signals, vulnerability findings, and infrastructure-as-code (IaC) misconfigurations to build a complete picture of application security. This visibility makes it easy to trace the source of an exposure, revoke affected keys, and implement policies to prevent similar incidents.
Get started with Secret Scanning and Code Security
Secret Scanning helps you protect your codebases by detecting, validating, and blocking exposed credentials before they can lead to a security incident. It continuously monitors your repositories and CI/CD pipelines for leaked secrets and integrates with developer workflows to stop sensitive data from being committed.
Secret Scanning is one part of Datadog Code Security, which provides a unified view of risk across the software development life cycle. Code Security also includes Software Composition Analysis (SCA) to identify vulnerable dependencies, Static Code Analysis (SAST) and Runtime Code Analysis (IAST) to uncover vulnerabilities in custom code, and IaC Security to detect misconfigurations in deployment templates and cloud resources.
To learn more, check out our Secret Scanning documentation and Code Security documentation. If you’re new to Datadog, you can sign up for a 14-day free trial.