Barry Eom

Zach Groves

Will Potts

Will Roper
With the rise of generative AI (GenAI) workloads, engineering and platform teams continue to standardize observability around OpenTelemetry (OTel) to unify application, infrastructure, and AI workload visibility. OpenTelemetry gives them a single, governed pipeline for telemetry, where processors can redact, enrich, and route data before it leaves the network.
OTel GenAI Semantic Conventions establishes a standard schema for tracking prompts, model responses, token usage, tool/agent calls, and provider metadata. By defining a consistent vocabulary for spans, metrics, and events across any GenAI system, these conventions make AI observability measurable, comparable, and interoperable across frameworks and vendors.
Until now, Datadog LLM Observability data required Datadog’s SDK or teams to submit manually annotated spans directly to the HTTP API intake, meaning teams that adopted OTel had to maintain parallel instrumentation paths or bypass collector-level policies. That’s why Datadog now natively supports OpenTelemetry GenAI Semantic Conventions (v1.37 and up), allowing you to instrument your LLM applications once with OTel, export OTel GenAI spans via your existing OTel Collector pipeline or directly into the Datadog Agent in OTLP mode, and analyze GenAI spans directly in LLM Observability, with no code changes required.
In this post, we’ll cover how to send governed OTel GenAI spans from the OTel Collector or Datadog Agent to Datadog, and how you can unify performance, quality, and cost metrics across all your GenAI workloads.
Send OTel GenAI spans to Datadog
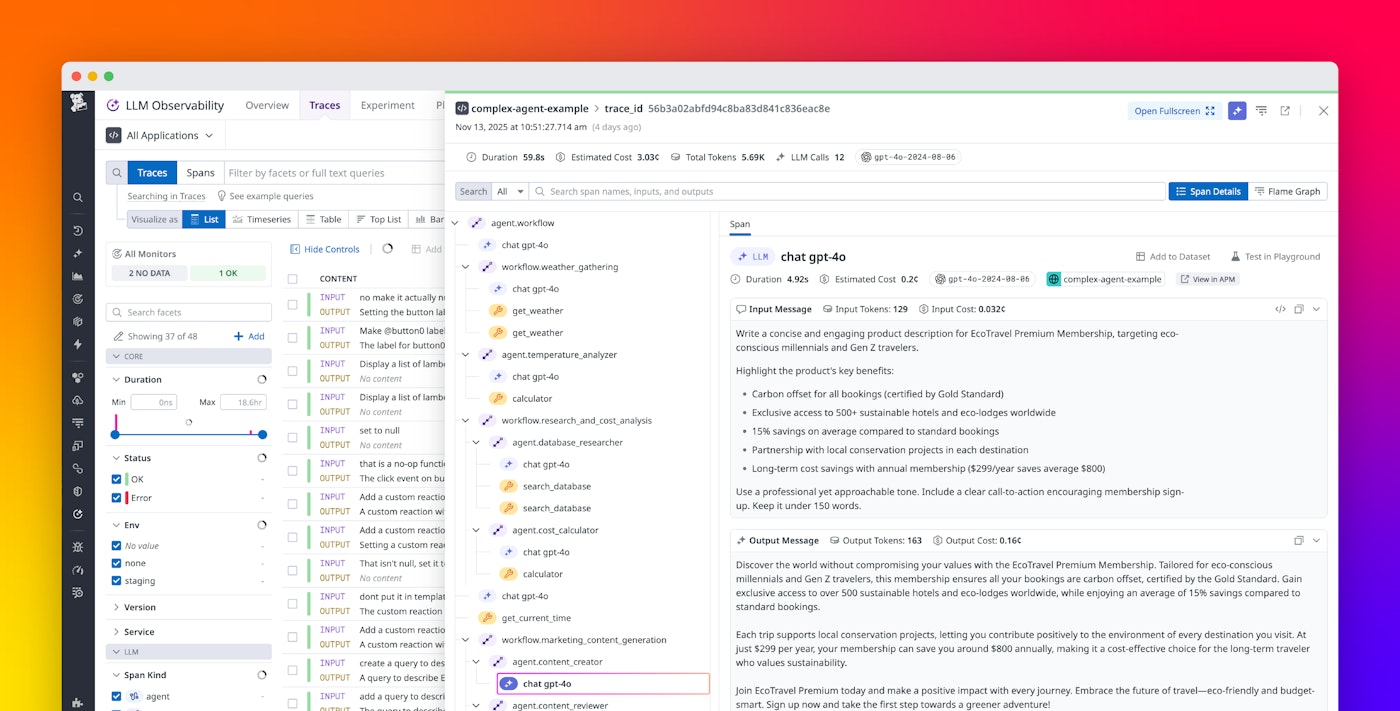
With Datadog’s native support for OTel GenAI Semantic Conventions, teams can forward GenAI spans directly into Datadog LLM Observability without duplicating instrumentation or bypassing governance policies. You can start by instrumenting your application using any OTel-compatible SDK or framework that emits spans conforming to the GenAI Semantic Conventions v1.37 schema. These spans can describe prompts, completions, tool calls, or agent workflows, following the standardized attribute names defined in the OTel documentation.
Once your application is emitting GenAI spans, you can send them to Datadog LLM Observability using several OTLP-based options: directly from your OTLP exporter to Datadog’s OTLP intake endpoint, via the Datadog Agent with OTLP ingest enabled, or through the OpenTelemetry Collector (including the Datadog Distribution of the OpenTelemetry Collector). When you use the Collector, you can apply processors for redaction, sampling, enrichment, and routing so your data policies are enforced before telemetry data leaves your network.
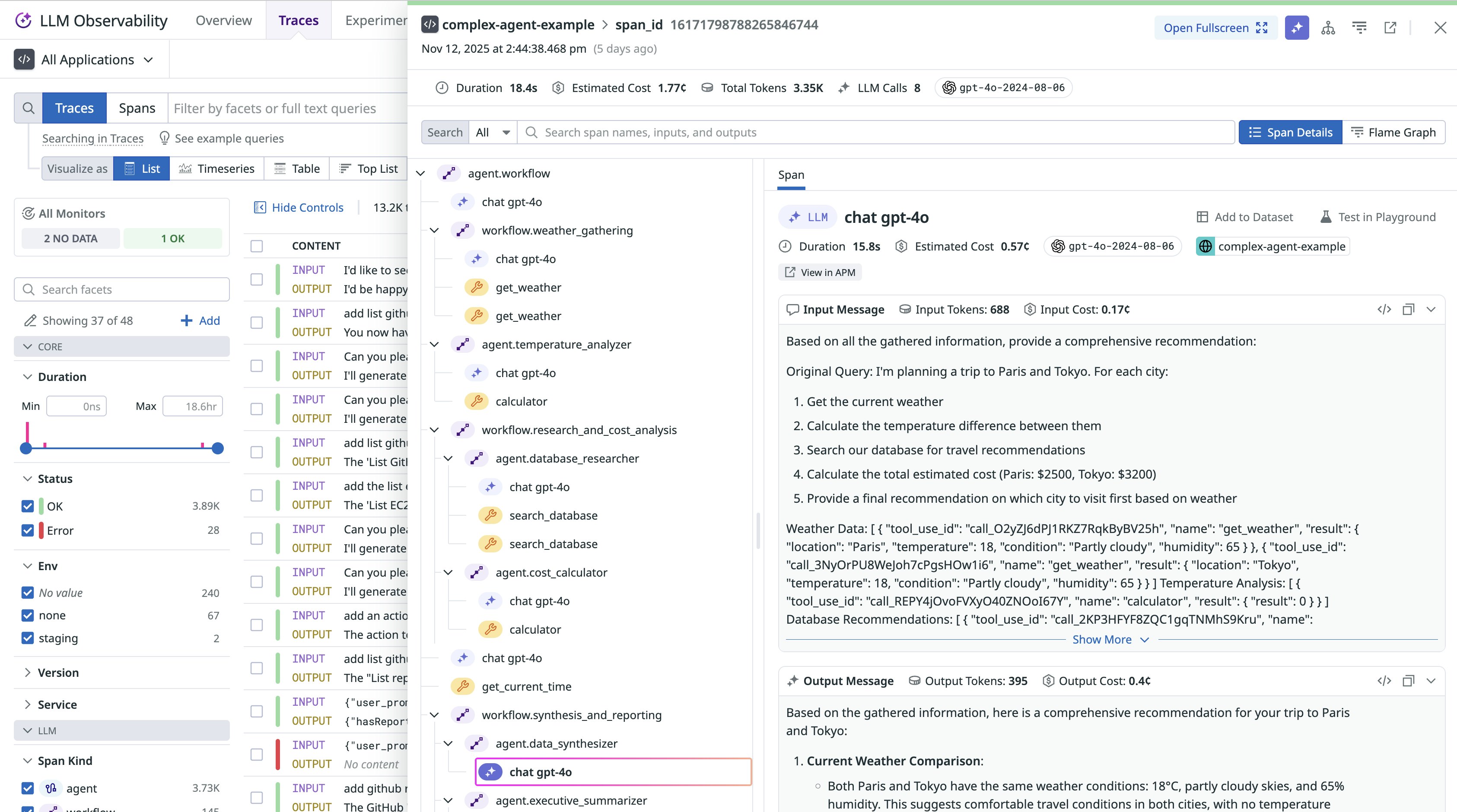
In all cases, Datadog automatically maps GenAI attributes (e.g., gen_ai.request.model, gen_ai.usage.input_tokens, gen_ai.provider.name, and gen_ai.operation.name) to the native LLM Observability schema for latency, token usage, cost, model/provider, and finish reason. This enables you to view GenAI traces alongside your existing APM traces, logs, metrics, and runtime data for cross-layer correlation. This architecture ensures that governance policies remain centralized in the Collector while providing full visibility once data arrives in Datadog. The result is clean, standardized, and compliant GenAI telemetry data without any duplicate work.
Unify analysis of prompts, agents, and tools across providers
Once GenAI spans are ingested, Datadog LLM Observability enables rich analysis across all AI providers and frameworks. Mapped fields include the model name and provider (e.g., openai.gpt-4o, anthropic.claude-3, or amazon.bedrock.mistral), along with token usage metrics such as input_tokens, output_tokens, and total_tokens. They also capture latency and cost metrics derived from span duration and provider metadata, as well as finish reasons and details about tool or agent operations to provide comprehensive workflow visibility.
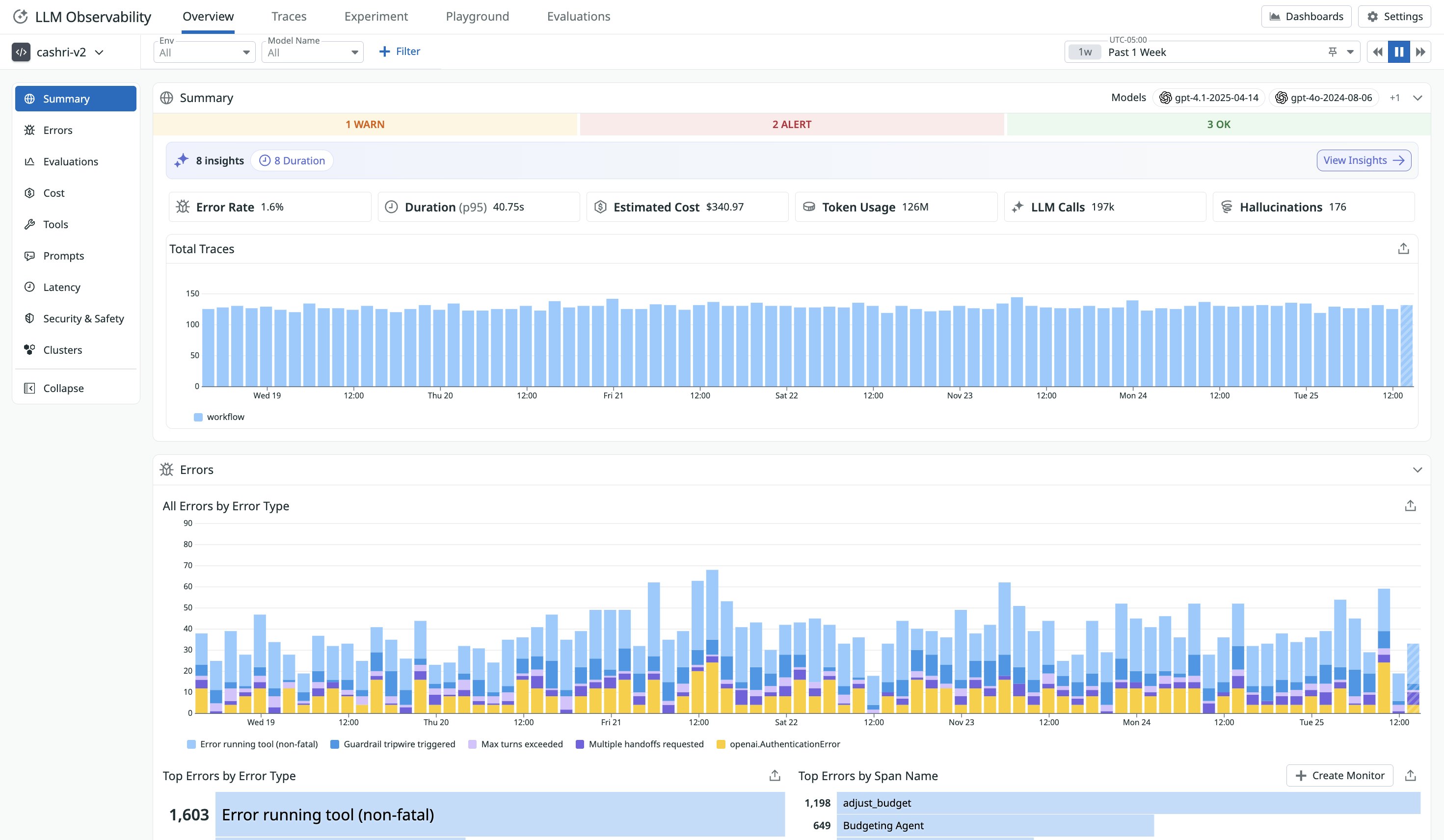
Once the traces are ingested into LLM Observability, AI engineers can analyze token usage, latency bottlenecks, and cost to evaluate input/output efficiency and spending patterns across specific models and providers. After identifying issues to investigate in LLM Observability, AI engineers can pinpoint the execution step or function call at the root cause of an unexpected response. They can also view the input (prompt and user message) and output of each LLM, workflow, and agent operations for further troubleshooting.
You can further break down telemetry data by model and provider, using fields such as gen_ai.request.model and gen_ai.provider.name to compare performance results across vendors such as OpenAI, Anthropic, and Amazon Bedrock. For multi-agent or tool-based frameworks, attributes such as gen_ai.operation.name (e.g., tool_call or agent_run) let you trace end-to-end agent and tool flows within orchestrated AI systems. And because this data flows into the same observability backend, engineers can correlate GenAI spans with full-stack APM traces, linking an individual prompt to a broader user transaction or service request.
In addition, LLM Observability helps you close the loop between production and experimentation so you can iterate on agentic applications faster. You can promote interesting production traces into curated, version-controlled datasets—i.e., your “golden” test sets of real-world prompts, outputs, and span context—and extend them with annotations and evaluation metadata. Using the LLM Experiments SDK or submitting your experiments directly to the HTTP API, you can then run repeatable experiments on these datasets to compare prompts, parameters, models, and agent strategies while automatically collecting span-level telemetry data and evaluation scores in LLM Observability.
Standardize on OTel for GenAI with Datadog
With native OTel GenAI SemConv support, Datadog LLM Observability enables teams to monitor and improve AI systems while maintaining their existing observability and compliance workflows. Teams can instrument once using the OTel GenAI Semantic Convention (v1.37) and preserve governance through their OTel Collector’s processors. They can then analyze anywhere, as Datadog automatically maps and visualizes GenAI spans.
To get started, upgrade to OTel SDK/Collector v1.37 or later, then configure your OTLP exporter to send data to Datadog. Once set up, you can review your mapped spans and dashboards in Datadog LLM Observability.
If you’re new to Datadog, sign up for a 14-day free trial.