Kassen Qian

Daniel Blazquez
As development teams adopt generative AI at an unprecedented pace, security teams face an evolving set of challenges in securing the software development life cycle. The increasing speed and scale of code changes make it more difficult for organizations to manage risk effectively. Legacy scanners often fail to keep up, returning slow results and noisy alerts that increase remediation time and leave organizations exposed to potential breaches.
Datadog Code Security addresses these challenges by combining static and runtime analysis with AI-driven automation. Code Security continuously scans repositories for first-party code and open source dependencies, leaked secrets, infrastructure-as-code (IaC) misconfigurations, and malicious code patterns. It helps teams detect issues early and remediate them quickly while maintaining development velocity.
In this post, we’ll show you how Code Security uses AI to:
- Detect hidden code vulnerabilities
- Validate findings by filtering out false positives
- Remediate code vulnerabilities in batches
Detect hidden code vulnerabilities
Code Security continuously analyzes your codebase to identify vulnerabilities and suspicious code changes across repositories and services. In addition to performing traditional static analysis that relies on rule-based pattern matching, Code Security interprets code intent the way a security analyst would, identifying potentially malicious code changes in pull requests (PRs) that can introduce supply chain compromises. By breaking large code changes into smaller, interpretable chunks, Datadog’s AI-based detection achieves high precision and reduces alert fatigue for security teams.
For example, when a developer submits a PR, Code Security uses LLMs to evaluate code behavior in context. The code-review system has been trained on real-world examples of benign and malicious changes, such as dependency injections and tampered configurations, to identify risky diffs and alert security teams before the code change is merged. This approach draws on our internal security team’s ongoing engineering research into malicious PR detection, which has shown that LLMs can detect subtle signs of harmful intent that traditional static analyzers often miss.
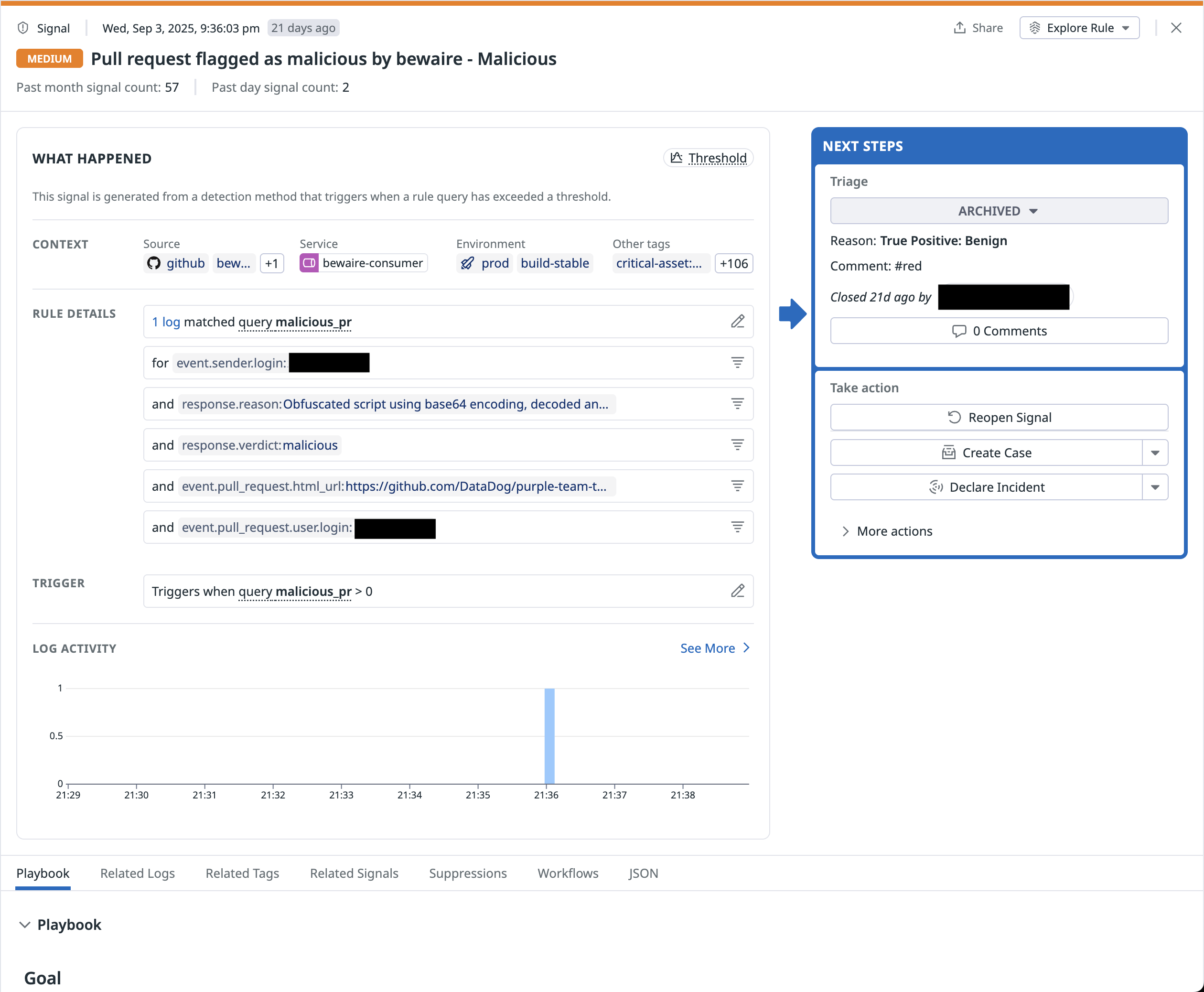
Prioritize high-risk findings by filtering out false positives
Static analysis tools often overwhelm teams with false positives, leading to alert fatigue and slower remediation. Code Security now incorporates false positive filtering to automatically validate vulnerability findings.
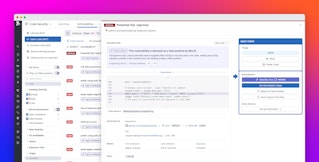
Each detected vulnerability appears in the SAST Vulnerabilities Explorer and is labeled with a confidence score, such as High Confidence or False Positive. You can filter findings by confidence level by using the Bits AI Assessment facet, or you can toggle off false positives entirely to focus on the most actionable issues.
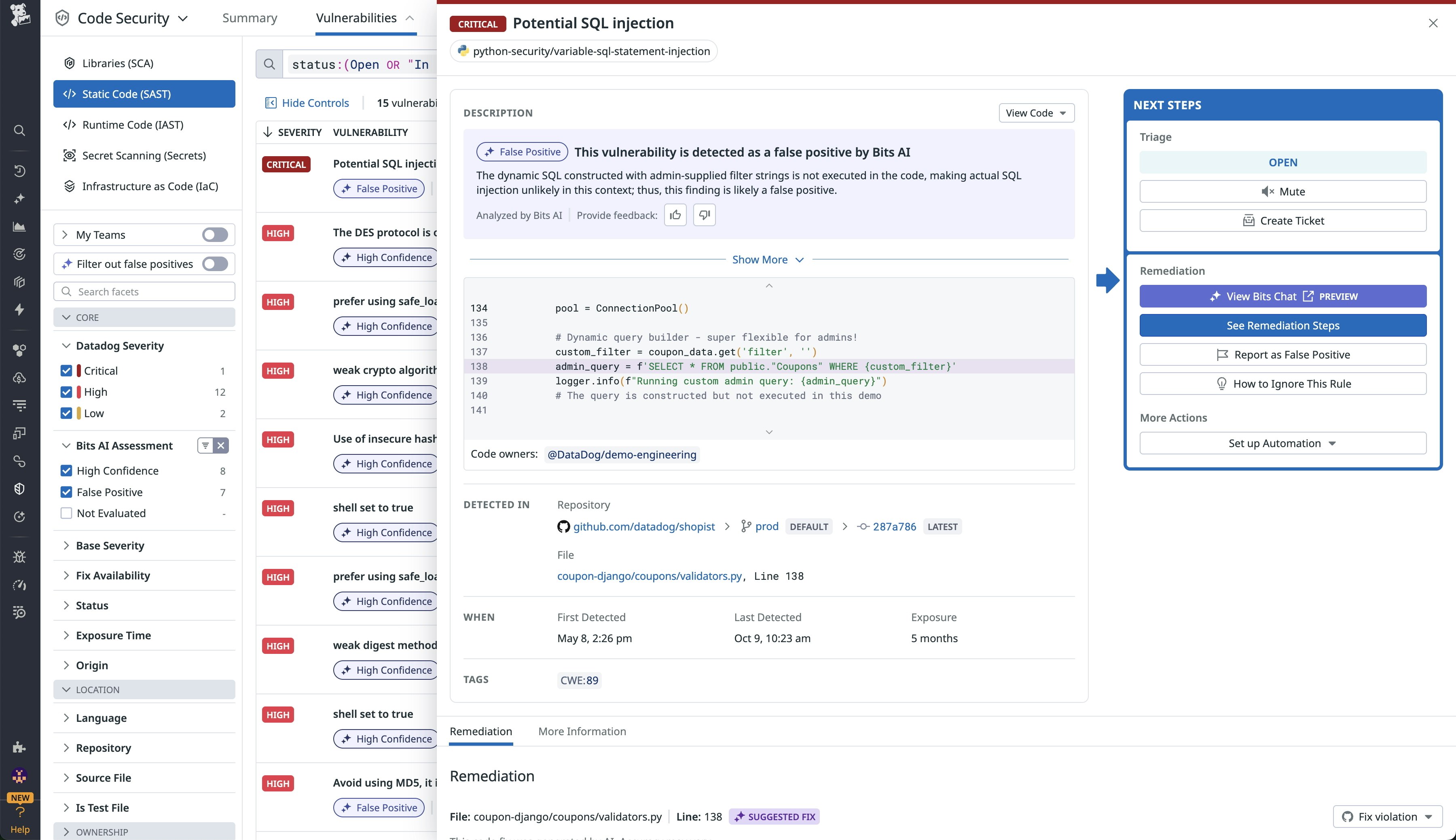
You can view the reasoning behind each classification in the vulnerability’s side panel. This transparency enables you to verify the assessment and provide feedback that improves future assessments. By automatically identifying which findings are false positives, such as the potential SQL injection vulnerability in the following screenshot, Code Security reduces time spent on non-issues and helps you prioritize high-risk vulnerabilities.
Remediate code vulnerabilities in batches
After vulnerabilities are detected, the next challenge is resolving them efficiently and at scale. Code Security simplifies this process by turning AI into an active collaborator that helps you fix issues faster.
Using Bits AI, developers can automatically generate proposed code patches for detected code vulnerabilities. They can create fixes for each individual vulnerability or for batches of vulnerabilities. The Bits AI Dev Agent presents each generated remediation as an editable suggestion, enabling developers to review and refine fixes before they’re applied back to the codebase. This approach keeps engineers in full control of remediations while reducing repetitive manual effort.
In the following example, Bits AI shares how it fixed two instances of SQL injections in the same file. You can give Bits AI direct feedback to modify the generated remediations before creating a PR.
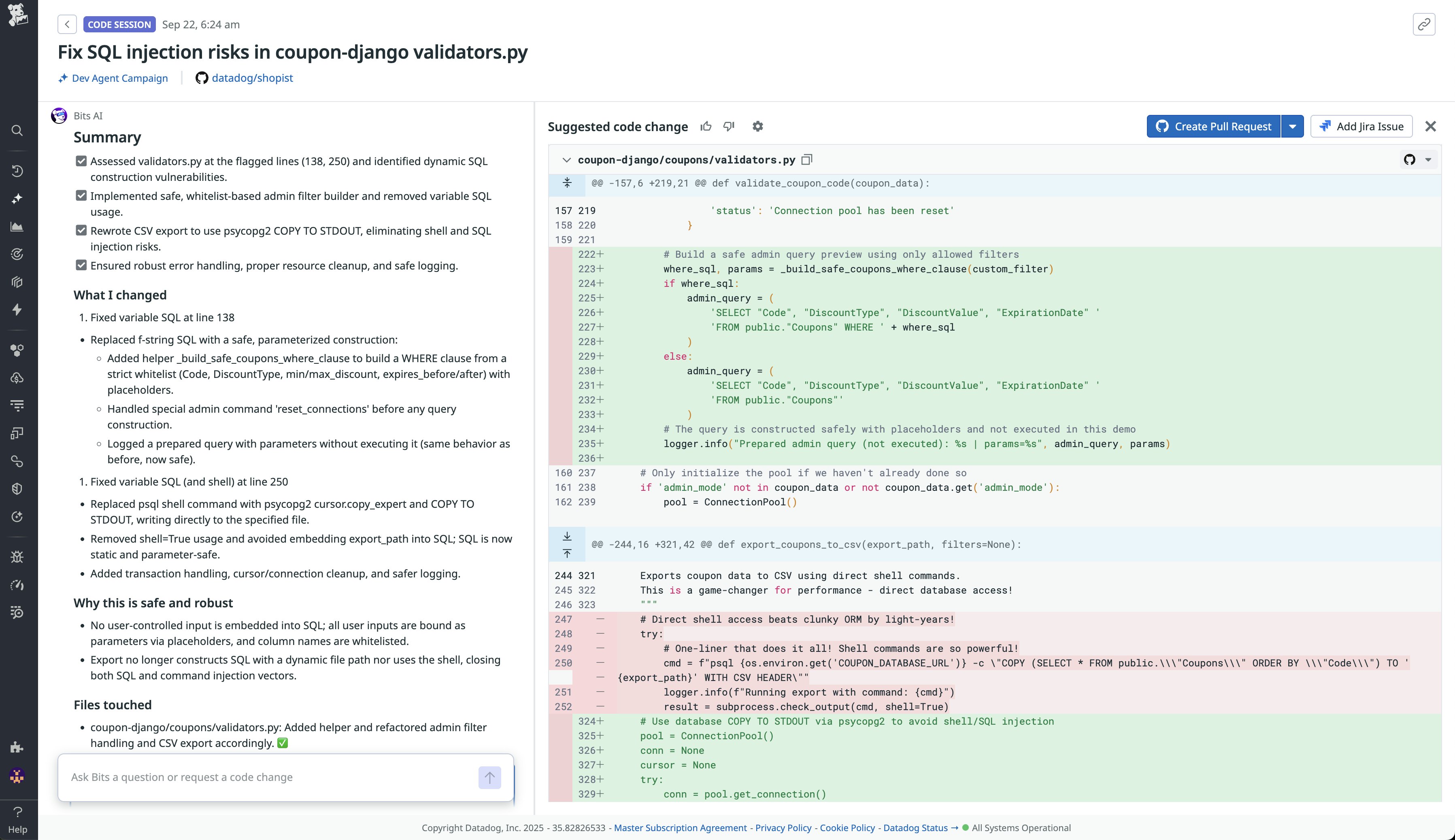
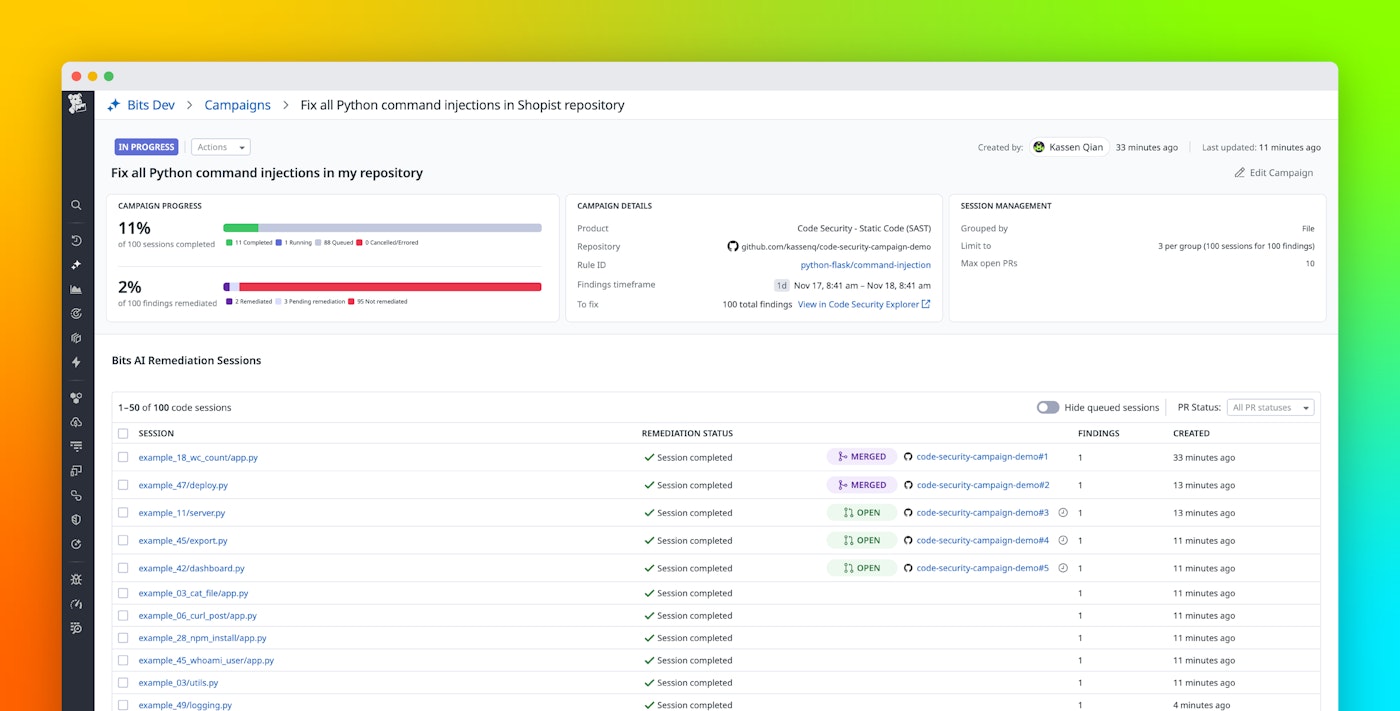
Batched remediation helps teams address vulnerabilities in bulk and groups multiple related fixes into generated PRs. This approach mirrors how experienced engineers resolve correlated issues, reducing friction and minimizing redundant changes. Teams can track the progress of remediation campaigns directly within the Datadog UI.
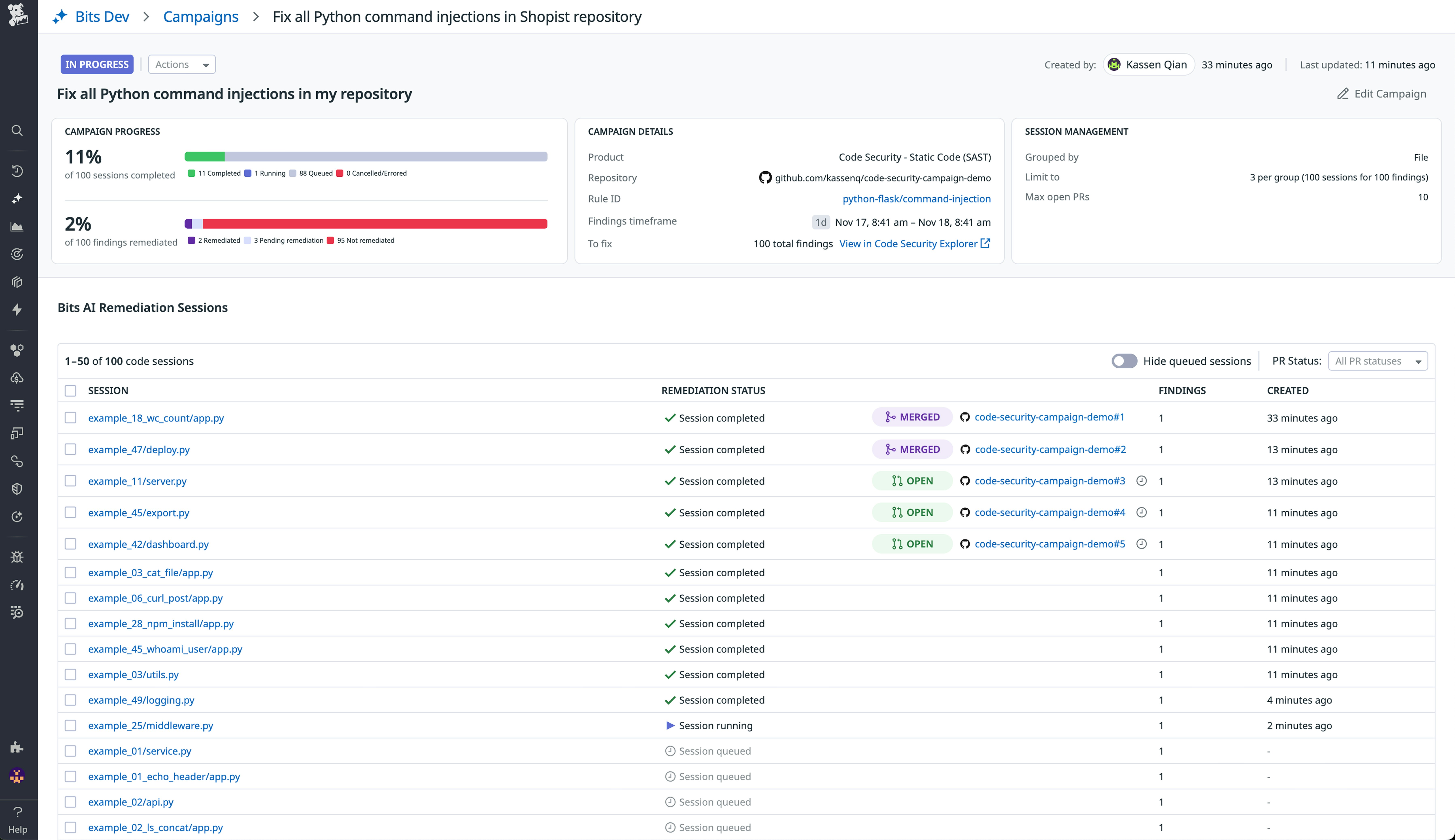
Whether you take the individual or batched approach, Code Security tracks every remediation (the generated fix and associated PR status) to give your teams a unified view of progress and ownership across repositories. By embedding remediation into the same environment where vulnerabilities are detected and analyzed, Code Security helps reduce mean time to resolution (MTTR) without disrupting developers’ daily work.
Implement modern code security for modern development
As AI-native coding tools become increasingly common, traditional manual triage and scanning methods must be combined with AI-driven vulnerability management practices to help security and development teams keep pace. Code Security offers a modern approach to securing your applications, blending a focus on developer experience with AI-native analysis to help teams detect, validate, and remediate vulnerabilities quickly and safely.
To learn more, check out the Code Security documentation. You can also request access to these new capabilities in the Preview form for Bits AI Dev Agent (for batched remediation) and the Preview form for malicious PR protection.
If you’re new to Datadog, sign up for a 14-day free trial to get started.