The complex and distributed nature of cloud computing has created a new paradigm for security. Every part of an organization now has a hand in mitigating security risks, from developers addressing misconfigurations in infrastructure as code (IaC) to identity and access management (IAM) teams downsizing the permissions of cloud roles that have non-essential access to sensitive data.
A cloud-native application protection platform (CNAPP) offers an integrated security tool that fosters a culture of shared security ownership. CNAPPs help teams by enhancing visibility, prioritizing risks, demonstrating continuous compliance, and ensuring the deployment of fixes to production. They also help reduce the risk of misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and overprivileged identities that could impact critical infrastructure and compromise sensitive data.
This guide discusses how CNAPPs work, explores some of their most important use cases, and identifies essential features to look for when choosing a CNAPP solution.
What is a CNAPP?
A CNAPP is a unified security solution designed to protect applications built and run in cloud environments. CNAPPs provide comprehensive security across the entire lifecycle of cloud-native applications—from development through production. With CNAPPs, teams gain complete visibility across their clouds. CNAPPs are also able to layer in context from the organization’s infrastructure to better prioritize risks.
For example, a CNAPP should be able to send an alert if a misconfiguration on an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance could allow an attacker to access sensitive data. CNAPPs also allow cloud security teams to more easily coordinate with DevOps and engineering teams to deploy critical security fixes to production. By integrating security broadly across development and production, CNAPPs shift security from a potential business blocker to a business enabler, ensuring reliability and uptime of critical cloud infrastructure. Read more about Datadog’s CNAPP platform where teams can detect and protect throughout the software development lifecycle.
What industry shifts are driving CNAPP adoption?
Traditionally, on-premises IT systems have been isolated in different silos depending on the department or function, each with its own management and security protocols. The cloud changed this: previously isolated domains are now a cohesive environment connected by infrastructure and applications. At the same time, organizations have moved away from building applications as single, monolithic entities to developing and deploying apps using containers and microservices.
These shifts have led to a more complex and distributed IT infrastructure, significantly expanding the scope of security requirements. Security is no longer just the job of the InfoSec team; now, combined DevOps, engineering, and security teams play an essential role. These changes drive the need for an integrated security platform that can be used across security, DevOps, and engineering teams. CNAPPs are designed to meet this need and help organizations achieve DevSecOps.
Why is a CNAPP important?
Cloud computing has driven the need for a unified security solution that can be used not only by security teams but also by DevOps and engineering. A CNAPP offers several essential benefits to help meet this need:
Breaking down organizational silos: CNAPPs provide essential cross-domain visibility, allowing organizations to see where vulnerabilities might be exploited to create attack paths. Enhancing visibility in cloud environments. As cloud environments become increasingly dynamic, maintaining a real-time inventory of cloud resources presents a significant challenge. CNAPPs address this by offering tools that can continuously monitor and catalog every cloud resource in real time.
Managing alert fatigue: With potentially hundreds of thousands of resources to monitor, each generating its own set of alerts, security teams can quickly become overwhelmed. CNAPPs help streamline these alerts by consolidating and prioritizing them according to criticality and potential impact.
Streamlining remediation processes: CNAPPs facilitate better collaboration across security, DevOps, and engineering teams by providing clear guidelines for remediation. Critical security updates are expedited from identification to implementation, which helps provide the cloud environment with more robust security.
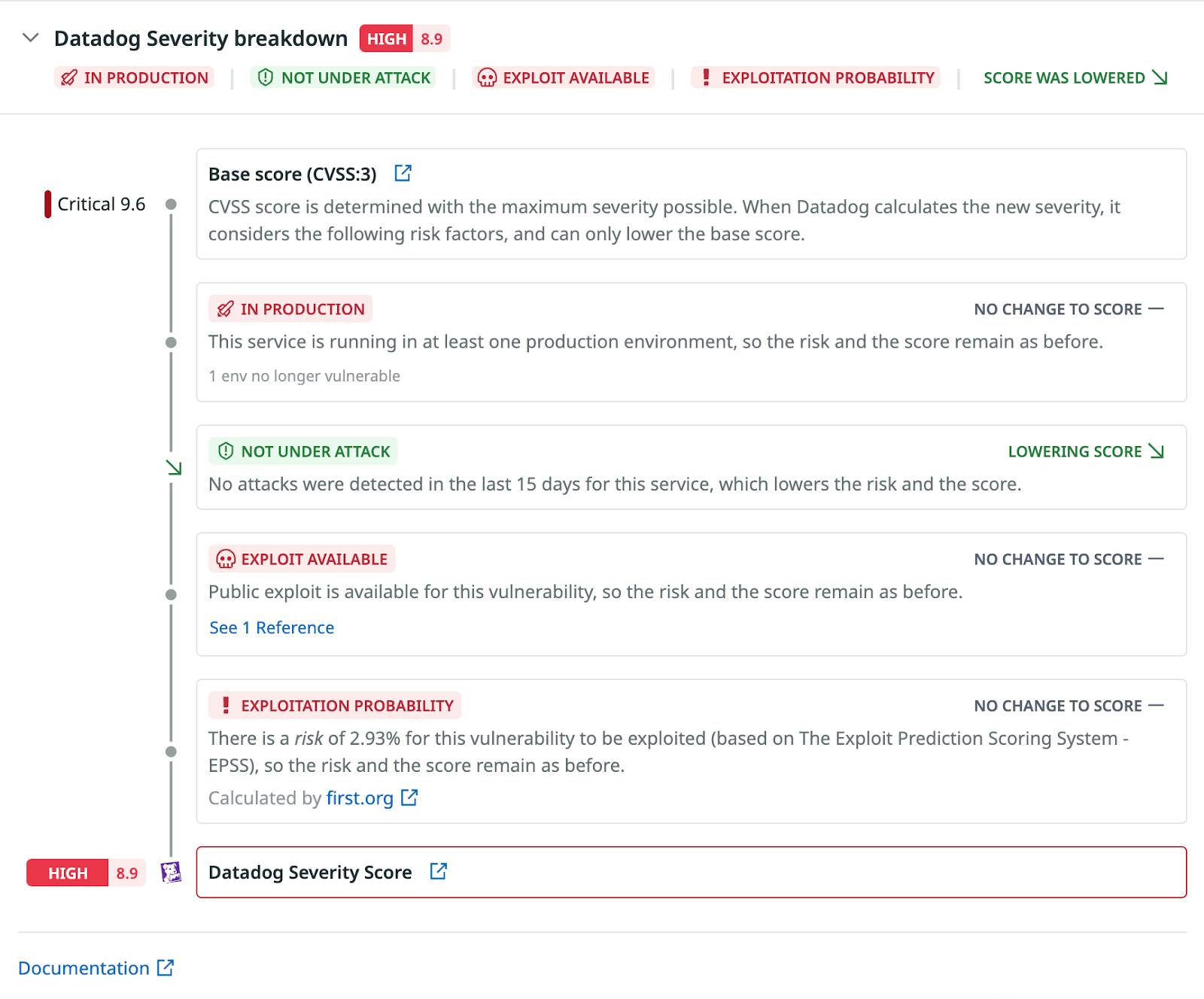
Prioritizing alerts: CNAPPs are not only capable of monitoring processes, resources, and workflows, they are also able to identify and prioritize the severity of events (see Figure 1 for an example of a severity score). This means teams are better equipped to manage and address alerts.
How does a CNAPP work?
CNAPPs enhance cloud security by providing a unified interface that reveals key security insights, including identity risks, vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and data exposure through agentless and agent-based scanning methods.
Agentless scanning: To perform agentless scanning, a CNAPP uses cloud-provider APIs to periodically capture snapshots of an environment. For instance, an agentless scanner might collect snapshots of virtual machine (VM) instances and Amazon Web Services (AWS) Lambda code dependencies. These snapshots could be scanned to identify vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. After scanning, the snapshots would be deleted to ensure no confidential or personal information remains in the infrastructure. Agentless scanning offers broad coverage and is particularly effective for ephemeral cloud resources. It’s also straightforward to implement and manage.
Agent-based scanning: A CNAPP uses agent-based scanning for resources that need more detailed and real-time monitoring. This approach involves deploying agents directly on hosts or within containerized environments, where they continuously collect in-depth event data and metrics. This method is crucial for achieving granular control and real-time threat detection.
Integration and prioritization: Some CNAPPs support both scanning types, ensuring comprehensive visibility and control over complex cloud environments. A good CNAPP can deploy a single agent that gathers both security and observability data to simplify management and enrich the security context. This integration allows the CNAPP to prioritize findings more effectively by considering their interrelationships with other risks and their impact on runtime operations. For example, instead of merely ranking vulnerabilities by their Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) score, a CNAPP could evaluate vulnerabilities within the broader context of an environment—such as the criticality of the affected system, its access to sensitive data, its likelihood of exploitation, and its connection with other vulnerabilities or misconfigurations to form viable attack paths.
What are the key use cases for a CNAPP?
CNAPPs streamline cloud security in dynamic multicloud environments for various use cases.
Maintain continuous visibility: A CNAPP offers comprehensive and ongoing visibility into cloud operations, spanning multiple cloud platforms. It continuously discovers, catalogs, and monitors cloud resources; identifies risks across infrastructure, workloads, identities, and data; and visualizes this information in a unified dashboard. This enables organizations to spot potential security risks before they impact customers.
Govern access and right-size permissions: By continually scanning cloud infrastructures, a CNAPP identifies and mitigates entitlement risks such as excessive administrative privileges, privilege escalations, and overly broad access rights, including risky cross-account accesses. CNAPPs can help organizations proactively spot and rectify IAM vulnerabilities, safeguarding against IAM-based cyber threats. They can also suggest downsized policies, workflow blueprints that automate cross-functional response, and remediation instructions specific to a cloud provider.
Manage vulnerabilities across the stack: A CNAPP enables the discovery, prioritization, and remediation of vulnerabilities across container images, hosts, host images, and serverless functions, from the development phase in continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines to deployment and runtime. It also prioritizes vulnerabilities based on the context of the environment—considering factors like workload criticality and severity. A CNAPP can use observability data to guide users on where vulnerabilities are most critical, what should be addressed first, and which teams need to be involved in the remediation process.
Identify and secure sensitive data in cloud storage: Cybercriminals target sensitive information such as personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), and intellectual property (IP). A CNAPP helps pinpoint the location of sensitive data within a cloud environment. The CNAPP also identifies potential pathways attackers might exploit to help security teams prioritize their efforts to protect against those vectors.
Report on compliance posture and maintain adherence to regulatory requirements: Organizations need to demonstrate continuous compliance with multiple regulatory frameworks. A CNAPP simplifies and accelerates this process by providing out-of-the-box compliance reports for risk and compliance teams that show current security and compliance status and track improvements over time.
Foster collaboration between DevOps and security teams with a single source of truth: A CNAPP is a central hub for DevOps and security teams, offering shared visibility into the cloud risk posture. Tools integrate seamlessly into existing workflows, democratizing access to security insights and remediation capabilities.
What are the challenges in implementing a CNAPP?
In considering a CNAPP, an organization must understand there will be specific challenges to ensure a smooth implementation. These challenges include:
Organizational alignment: Cross-functional teams must support the implementation. This includes aligning security goals to business objectives such as uptime, site reliability, and compliance.
Tool sprawl: Consolidate tools wherever possible by integrating CNAPP platforms with security information and event management (SIEM) and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) tools.
Complexity: Many CNAPP solutions provide myriad features that can complicate workflows, slow development, and generate noise.
To overcome these challenges and successfully adopt a CNAPP, be sure to manage effectively across teams to achieve alignment, choose a CNAPP that integrates with native development and operational tools, and start out by implementing mission-critical features first.
What features should you look for in a CNAPP?
When considering a CNAPP, organizations should identify features like:
Unified security and observability: Look for a CNAPP with security and observability integration within a single application, allowing administrators to access security insights and operational metrics from one platform. Security findings should be enriched with runtime context identifying if an affected resource is in production, or if it’s connected to a revenue-impacting service.
Agentless and agent-based scanning: Understand the benefits of agentless and agent-based scanning and find a platform with both.
A single agent: Find a CNAPP that can deploy one agent to collect both security and observability insights to reduce overhead and ensure multilayered runtime context for prioritization.
Easy onboarding: Confirm that CNAPP onboarding is simple. Deploying the CNAPP should take a reasonably short time and should not require a team of professional services engineers.
No complex query language: CNAPPs should be intuitive tools that all parts of the organization can use to gain a view of cloud posture and risks.
Shared use across teams: Look for persona-based dashboards and confirm there is no set seat limit. This can help operationalize CNAPP use while ensuring users aren’t clouded by irrelevant data.
Tech integrations: Ensure the CNAPP integrates with existing tooling such as SIEM, SOAR, and code security solutions. CNAPP providers should have a breadth of integrations with cloud provider tooling, such as Amazon Inspector.
Real-time and proactive security: Ensure the CNAPP provides proactive security insights and real-time insight into active threats.
Compliance: Ensure the CNAPP provider is keeping up with evolving compliance regulations. CNAPPs should provide out-of-the-box compliance reporting and scoring against key regulatory frameworks like Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), Payment Card Industry (PCI), and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Breadth of features: A CNAPP should include the following solutions: cloud security posture management (CSPM), cloud infrastructure and entitlement management (CIEM), cloud vulnerability management, Kubernetes security posture management (KSPM), IaC scanning, data security posture management (DSPM), compliance, and vulnerability management.
When choosing a CNAPP, look for integrated observability and security, flexible scanning options, easy deployment and use, real-time security insights, and comprehensive tools that support cross-team collaboration.
Learn more
Using a CNAPP, organizations can secure and protect cloud-native applications across development and production. Learn more about CNAPPs: