Datadog Agent OTLP Receiver in Kubernetes
8月 6, 2025
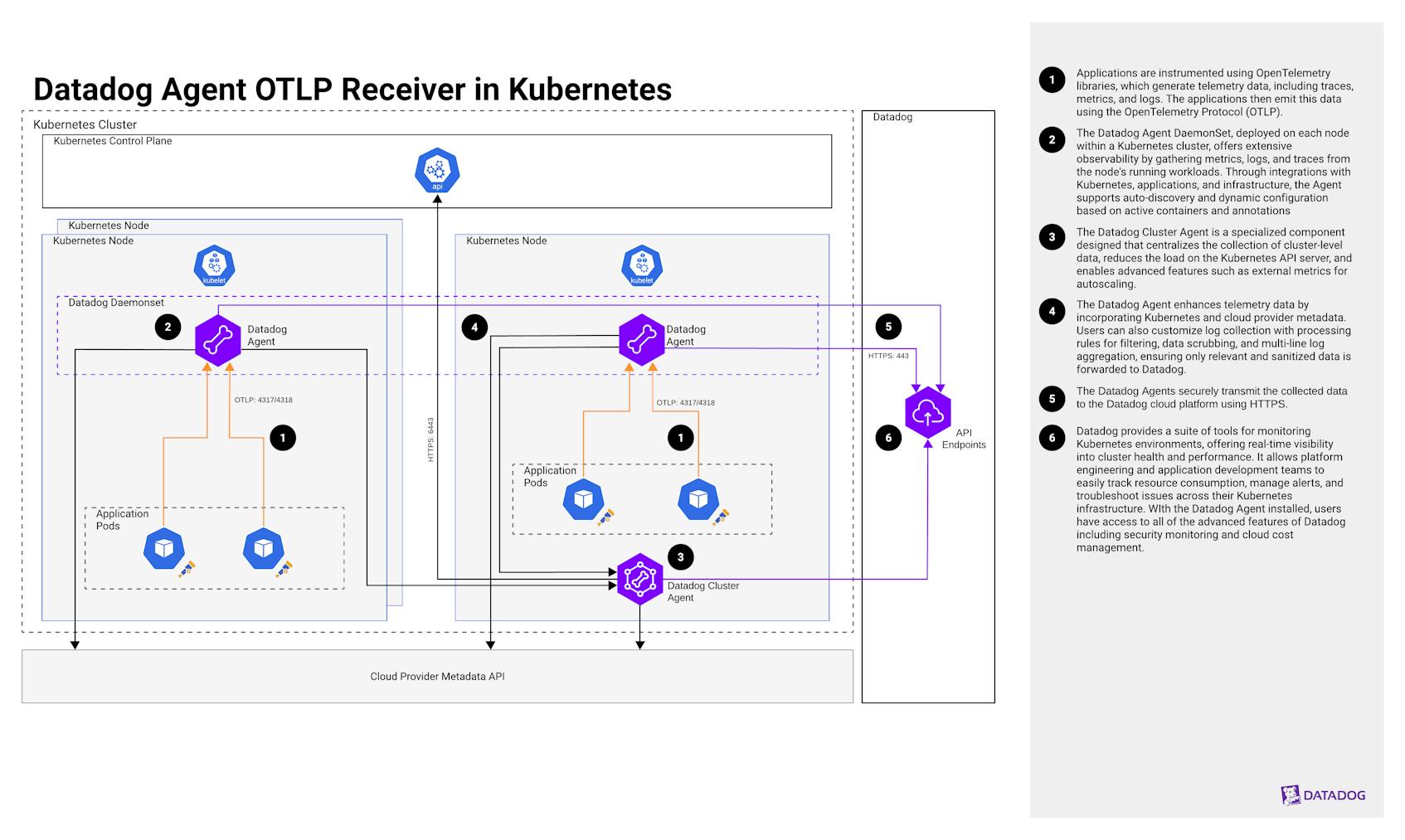
Intro
OpenTelemetry, with its vendor-agnostic approach, has emerged as the go-to open standard for generating and managing telemetry data. Instrumenting applications with OpenTelemetry SDKs allows for data portability, avoiding vendor lock-in and the need to reinstrument or redeploy when switching vendors. The Datadog Agent, with its built-in OpenTelemetry Protocol (OTLP) receiver, simplifies the collection and forwarding of this telemetry data to Datadog for visualization and analysis, offering a streamlined and efficient observability pipeline for Kubernetes environments. This architecture is well suited for users with existing Datadog environments who are looking to adopt OpenTelemetry tracing.
Explanation of the architecture
This architecture utilizes the Datadog Agent with an OTLP receiver in a Kubernetes cluster to collect telemetry data and forward it to Datadog. This approach is particularly suited for existing Datadog customers who want to receive telemetry data from OTel instrumented applications. The Datadog Agent can be managed using either the Helm chart or the Datadog Operator.
Step 1 Instrumentation
Applications are instrumented using OpenTelemetry libraries, which generate telemetry data, including traces, metrics, and logs. The applications then emit this data using OTLP.
Step 2 - Datadog Agent Daemonset
The Datadog Agent DaemonSet is deployed on every node in a Kubernetes cluster to collect metrics, logs, and traces from workloads running on those nodes. It integrates with Kubernetes, applications, and infrastructure components, providing comprehensive observability. The Agent supports auto-discovery and can dynamically configure itself based on running containers and annotations. Additionally, with over 1000 built-in integrations, the Datadog Agent can collect data from a wide range of popular technologies and services, further extending its monitoring capabilities.
Step 3 - Datadog Cluster Agent
The Datadog Cluster Agent collects cluster-level data from the Kubernetes control plane and acts as a proxy between the API server and node-based Agents, reducing the load on the API server. This centralized approach is particularly beneficial for large Kubernetes clusters with hundreds or thousands of nodes, as it allows for efficient caching of cluster metadata. Also, the Agent can optionally be configured as an external metrics provider for autoscaling.
Step 4 - Datadog Agent Processing
The Datadog Agent enriches telemetry data with Kubernetes metadata by attaching pod labels, annotations, namespaces, deployments, and node details using the Cluster Agent and Kubernetes API. The Datadog Agent also collects metadata from the cloud provider’s instance metadata service (IMDS)—including instance ID, type, region, and availability zone—to provide context for telemetry data. Additionally, it attaches autoscaling group details and resource tags, enabling better tracking of dynamic cloud workloads. Users can also customize log collection by setting up processing rules to filter logs, scrub sensitive data, and aggregate multi-line logs. These configurations ensure that only relevant and sanitized data is forwarded to Datadog.
Step 5 - Agent egress to SaaS
The Datadog Agent securely transmits the collected data to the Datadog platform using HTTPS.
Step 6 - Analysis and Monitoring
Datadog provides a suite of tools for monitoring Kubernetes environments, offering real-time visibility into cluster health and performance. It allows platform engineering and application development teams to easily track resource consumption, manage alerts, and troubleshoot issues across their Kubernetes infrastructure. With the Datadog Agent installed, users have access to all of the advanced features of Datadog, including Datadog Security and Cloud Cost Management.
Challenges
This method is a strong choice if you want a straightforward way to integrate OpenTelemetry with Datadog and use Datadog’s rich feature set, especially if your tech stack includes languages not natively supported by Datadog APM. By leveraging OpenTelemetry’s vendor-agnostic instrumentation and data collection capabilities, you can seamlessly integrate your application’s telemetry data with Datadog, unlocking a wealth of insights and monitoring capabilities.
However, this approach may not be the optimal choice for every scenario, and it cannot send telemetry data to OTLP destinations. If your requirements include custom destinations or the need to access specific features that are only available within Datadog APM, other approaches may be more suitable. For example, if your application is built using a language that Datadog APM natively supports, utilizing the dedicated Datadog APM client libraries might provide a more streamlined and feature-rich experience. These libraries often offer deeper integration with Datadog’s APM capabilities, including distributed tracing, code-level profiling, and service dependency mapping.
Authors
Kennon Kwok - Senior Product Solutions Architect