Observability Pipelines VM Deployment
January 30, 2026
Introduction
As environments grow in complexity and volume, teams need to reduce data sprawl, optimize costs, and maintain data quality across a wide range of sources and destinations. To address these challenges, Datadog Observability Pipelines uses pre-processing capabilities on-premises to help organizations manage, transform, and route log data at scale within their environment.
Observability Pipelines helps you control log volumes and costs by selecting only the most valuable logs before forwarding them to more expensive storage solutions. It also enables you to extract key metrics from logs on-prem before dropping the rest, enabling you to alert on the most important telemetry without sending unneeded data to your destination.
Deploying Datadog Observability Pipelines on virtual machines enables scalable, flexible, and efficient log processing across traditional or hybrid infrastructures. In this setup, you manage the deployment and scaling of Observability Pipelines Workers (OPWs) directly on VMs, where each worker aggregates, processes, and routes logs throughout your environment. Compared to using containerized environments, this approach provides greater control over resource allocation and network configuration while maintaining the same high-performance data processing capabilities.
Explanation of the architecture
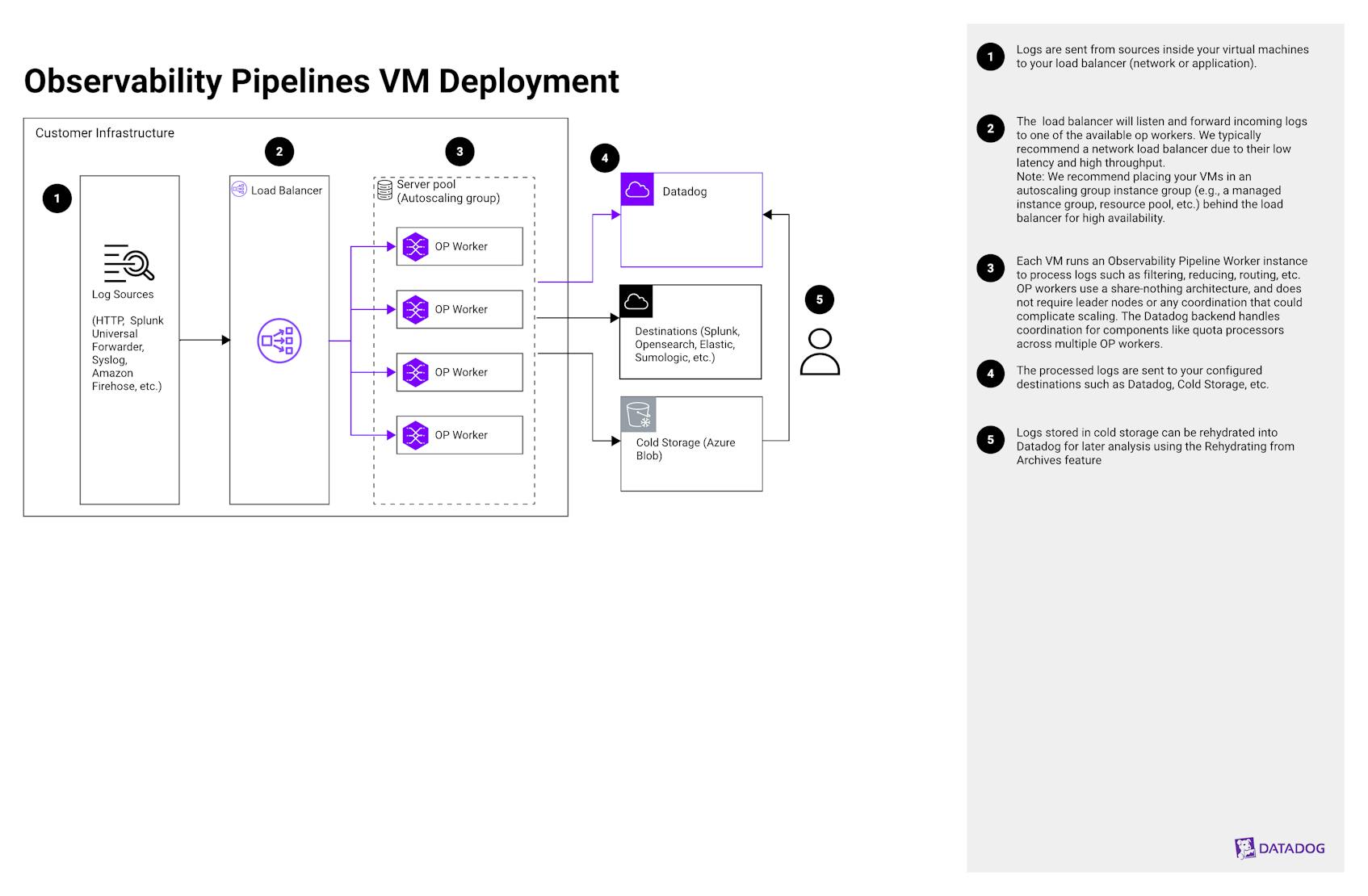
This architecture deploys Datadog Observability Pipelines on virtual machines to ingest, process, and route observability data at scale. It is useful for organizations that need fine-grained control over the volume, cost, and routing logic of telemetry data across hybrid or VM-based environments. In this architecture, a load balancer distributes logs from your log sources to OPWs running on VMs. Each worker filters, redacts, transforms, and routes data to configured destinations such as Datadog, third-party platforms, or cold storage.
This setup is well-suited for teams implementing cost optimization, compliance filtering, or multi-destination routing in VM or hybrid infrastructures. Additionally, in many organizations, teams might favor hosting Observability Pipelines in a VM because they have more experience managing and scaling VMs than they do with Kubernetes. Or, they might want to separate Observability Pipelines from their application clusters without running it in a dedicated Kubernetes cluster. (Note: When OP is hosted in a VM, the source logs can still originate in containerized workloads.)
Step 1
Logs are sent from any supported sources to your load balancer (network or application).
Step 2
The load balancer will listen and forward incoming logs to one of the available OPWs. We typically recommend a network load balancer due to their low latency and high throughput.
Note: We recommend placing your VMs in an instance group (such as an autoscaling group, managed instance group, virtual machine scale set, or service scaling group) behind the load balancer for high availability.
Step 3
Each VM runs an OPW instance to process logs such as filtering, reducing, routing, etc. OPWs use a share-nothing architecture, and does not require leader nodes or any coordination that could complicate scaling. The Datadog backend handles coordination for components like quota processors across multiple OPWs.
Step 4
The processed logs are sent to your configured destinations such as Datadog, cold storage, or any other supported destination.
Step 5
Logs sent to cold storage from Observability Pipelines are automatically sent in Datadogs rehydratable format. Logs stored in cold storage can be rehydrated into Datadog for later analysis by using the Rehydrating from Archives feature.
Key Benefits
- Log Volume Control: Manage logging costs by applying quotas and by filtering, sampling, splitting, and deduplicating logs to control which logs are sent to which destinations.
- Data Enrichment: Modify logs by adding, editing, or removing fields; including or excluding tags; and parsing unstructured logs into structured formats.
- Egress Cost Optimization: Minimize network egress and storage costs by extracting key metrics from logs on-prem before filtering and forwarding only the most relevant data to external or expensive storage solutions.
- Pre-Egress Data Redaction: Protect sensitive information by redacting personally identifiable or regulated data before it leaves your infrastructure to help you meet security and compliance requirements.